Coastal Waves
Aktis Hydraulics has considerable experience in-house with application of the following models:
- Wind seas, swells: SWAN
- Infragravity waves: 1DSB, SWASH
Aktis Hydraulics has considerable experience in-house with application of the following models:

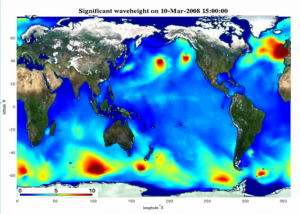
SWAN is an advanced coastal and regional scale spectral wave model. It is a two-dimensional, third-generation, spectral wave model. SWAN solves the energy balance equation in the computational domain. The wave energy is discretized in a frequency and directional domain at each node of the spatial computational grid, and allowed to propagate in space and evolve in time. The following wave processes can be represented in the model:

a one-dimensional wave model (spectral) used to model infra-gravity waves in the coastal zone. This may be used to provide boundary conditions for wave agitation models.

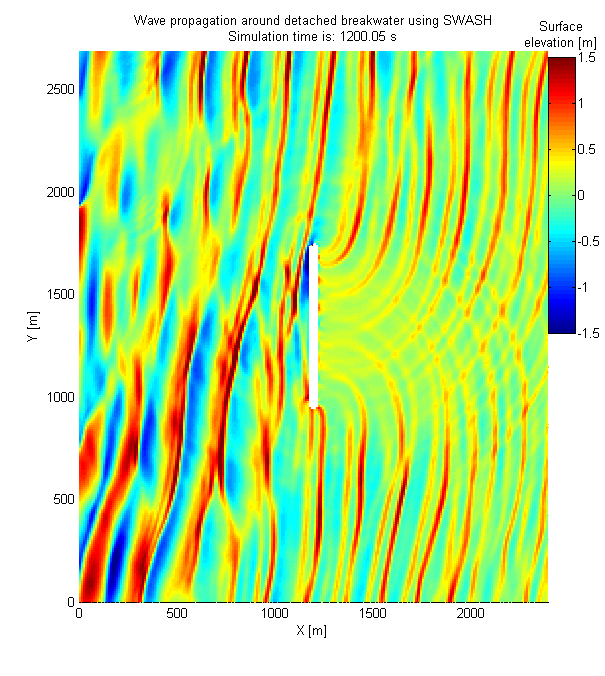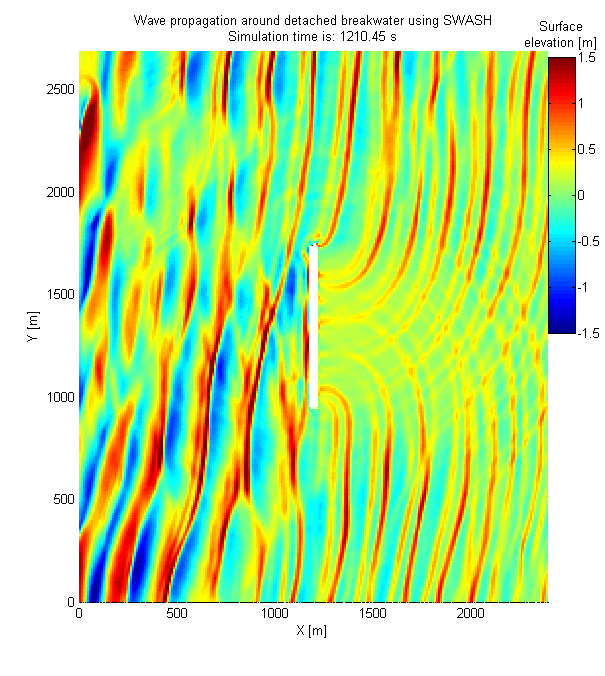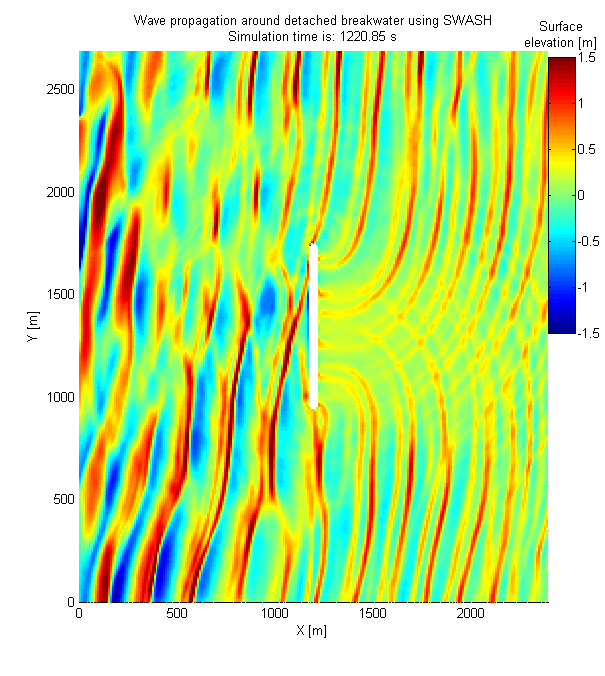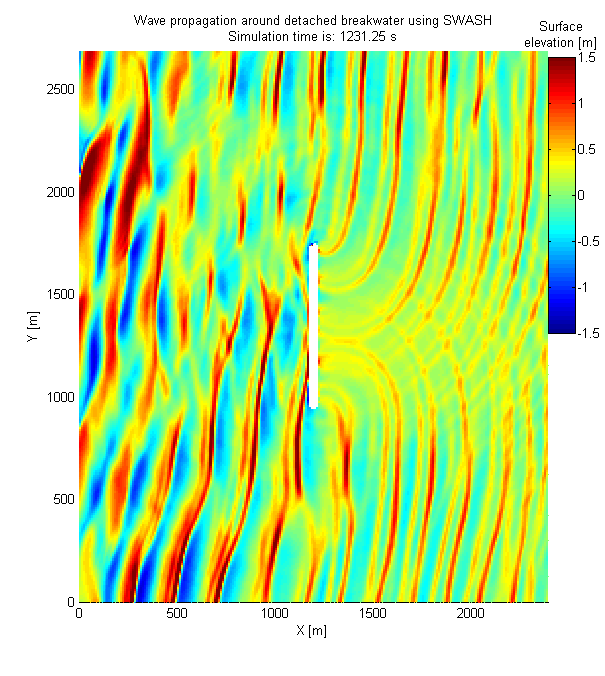
Aktis Hydraulics routinely uses SWASH to simulate water movements around structures and close to shore, including for evaluation of wave run-up on breakwater structures and evaluation of a (detached) breakwater shielding a terminal. SWASH has also been shown to be applicable for prediction of the generation and release of infra-gravity waves and for representing the effect of access channels on wave penetration more accurately than the models above (i.e. SWAN, PHAROS and TELEMAC).
SWASH accounts for refraction, shoaling, diffraction and reflection and is a time-domain model that automatically includes non-linear wave-wave interactions, bound long waves and the release of long wave energy at the tips of breakwaters or other structures that cause large gradients in the wave field. SWASH can also be applied for evaluation of Tsunami wave propagation, crest propagation and the hydrodynamic loads on large objects.